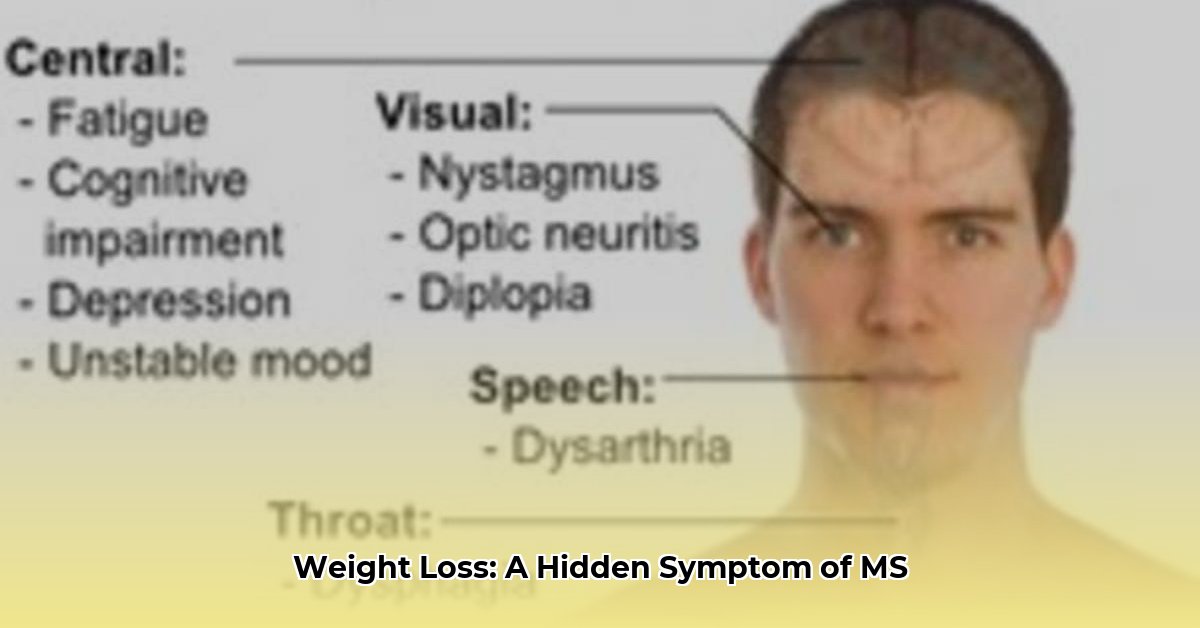
Does MS Impact Weight?
Multiple sclerosis (MS) can disrupt brain areas involved in metabolism and appetite, leading to weight changes.
Causes of Unintentional Weight Loss in MS
Muscle Loss: MS can weaken muscles, limiting movement and burning fewer calories.
Changes in Eating: Decreased appetite, swallowing difficulties, and nutrient malabsorption contribute to weight loss.
Fatigue and Shaking: Fatigue makes it difficult to cook and eat, while tremors hinder food preparation.
Medications: Side effects of MS medications, such as steroids and chemo drugs, can lead to weight loss.
How to Address Weight Loss in MS
- Medical Check-up: Rule out underlying medical conditions.
- Dietary Consultation: Develop a personalized meal plan that meets nutritional needs and addresses dietary challenges.
- Exercise: Maintain muscle mass and boost metabolism through regular exercise.
- Managing Fatigue: Prioritize activities, ask for support, and pace yourself.
- Emotional Support: Weight loss can be stressful. Seek support from therapists, groups, or loved ones.
Diet and Weight Changes in MS
MS can impact eating habits differently for each individual.
Weight Loss: Low energy, weak muscles, and appetite loss contribute to weight loss.
Weight Gain: Increased appetite from medications, reduced physical activity, and hormonal imbalances can lead to weight gain.
Managing Eating: Dietitians, exercise, medication adjustments, and emotional support can help manage weight in MS.
Physical Challenges and Nutritional Status
MS impacts weight and nutrition through physical challenges:
- Fatigue: Impairs daily activities and reduces appetite.
- Muscle Weakness: Reduces mobility and contributes to muscle loss.
- Coordination and Balance Issues: Makes eating and swallowing difficult.
Steps to Manage Weight and Nutrition in MS
- Healthcare Consultation: Seek guidance from doctors, dietitians, or other healthcare professionals.
- Nutritional Supplements: Consider supplements to ensure adequate nutrient intake when eating is challenging.
- Mealtime Simplification: Use assistive devices or modify recipes to make meals easier.
- Swallowing Difficulties: Consult speech therapists for strategies to improve swallowing.
- Fatigue Management: Implement energy-saving techniques and prioritize rest to reduce fatigue and improve appetite.
Remember, MS affects weight and nutrition differently for each individual. By understanding the underlying mechanisms and implementing appropriate strategies, individuals with MS can optimize their nutritional status and maintain a healthy weight.